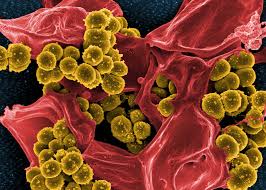
Introduction: The homoeopathic system of medicine is still considered as pseudoscience by the scientific community due to the lack of material substance in highly diluted medicinal formulations, despite clinical results. On the other hand, biomedicine is threatened by antimicrobial resistance against various pathogens. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a virulent strain of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, is resistant to several antibiotics like methicillin, nafcillin, oxacillin, and cephalosporins. In this study, homoeopathic nosodes also called biotherapeutic preparations, which are homoeopathic preparations made from pure microbiological cultures isolated from sick tissue and clinical samples like secretions, discharges, etc., were tested against MRSA to understand its antibacterial effects.
Method: Homoeopathic nosodes Anthracinum, Pyrogenium and Variolinum each in three different potencies namely 30 C, 200 C and 1 M were tested against MRSA by standardised Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion technique. Antibiotic vancomycin and dispensing alcohol were used as positive and negative control respectively.
Result: After the study, it was found that homoeopathic nosode Pyrogenium 200 C, Pyrogenium 1 M and Athracinum 200 C showed maximum inhibition zones of 11 mm, 10 mm and 10 mm respectively.
Conclusion: The results of this study indicate the efficacy of highly diluted homoeopathic medicines against the most virulent and threatening MRSA.