Introduction: An infectious or communicable disease (CD) is a condition triggered by an infectious agent or its byproducts that can be transmitted from one individual to another. A critical condition refers to a state of disorder that arises either during or following a regional conflict or a natural disaster, such as a flood or earthquake. Throughout emergency situations, the mortality rate due to infectious diseases can be 60 times higher than other causes, such as trauma. Over 40% of fatalities in emergency situations are caused by diarrhoeal illness, with children under the age of 2 years old accounting for 80% of these fatalities.
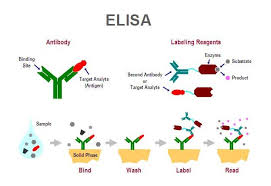
Method: The present study was conducted to understand the status of the common communicable diseases in children in Wasit Province, Iraq, during the years; 2018, 2019, and 2020. The study relied on retrospective data collected from the Department of Statistics at the General Teaching Hospital, Al-Kut City, Iraq. The study included thousands of children, who attended the hospital to seek medical attention due to suffering a CD. These subjects were tested using different types of ELISA methods.
Results: The results revealed a significant (p < 0.05) high spread of many CDs among children, such as mumps, chickenpox, cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis, hepatitis B, bacillary dysentery, and cutaneous anthrax. Some other CDs showed significant (p < 0.05) lower spread among children, such as acute flaccid paralysis, pertussis, and brucellosis.
Conclusion: The current study indicates important information about the status of the common communicable diseases in children in Wasit Province, Iraq, during the years 2018, 2019, and 2020.